Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) is a refined wood pulp product widely used in various industries, particularly in pharmaceuticals and food production. This versatile substance is known for its unique properties and numerous applications.
What is Microcrystalline Cellulose?
MCC is derived from fibrous plant material, primarily wood pulp. It is a purified, partially depolymerized cellulose that appears as a fine, white powder. The term “microcrystalline” refers to the tiny crystals that can only be seen under a microscope.
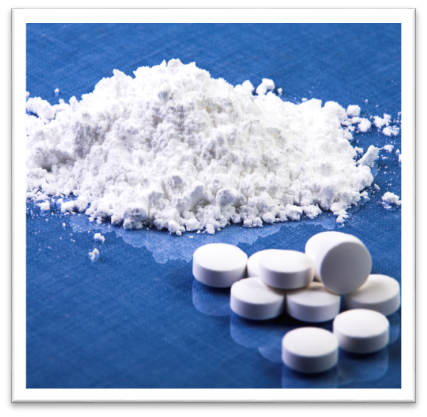


Applications in Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, MCC is valued for its binding properties. It is commonly used as an excipient in tablet formulations, helping to bind the ingredients together and ensure the tablet’s stability and integrity. MCC also acts as a disintegrant, aiding in the tablet’s breakdown and absorption in the body.

Applications in Food Industry
MCC serves multiple roles in food production. It acts as a texturizer, providing a desirable mouthfeel in various food products. Additionally, it functions as an anti-caking agent, preventing clumping in powdered foods. MCC is also used as a fat substitute, emulsifier, and bulking agent, contributing to the overall quality and consistency of food items.
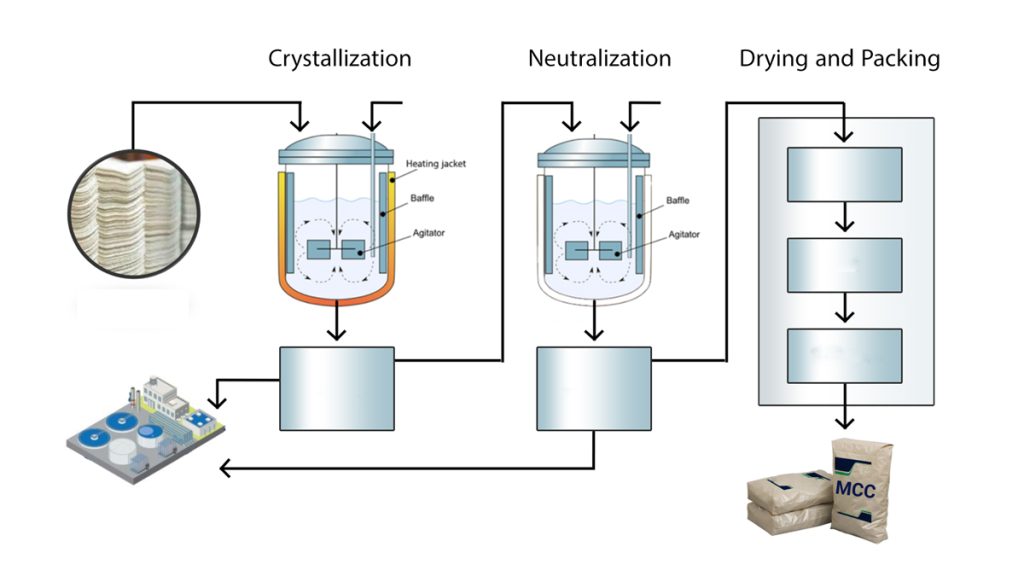
Production Process
The production of MCC involves the acid hydrolysis of cellulose. This process breaks down the cellulose into smaller, crystalline particles. Typically, hydrochloric acid is used at high temperatures to achieve this transformation.
1. Acid Hydrolysis
The cellulose is treated with an acid solution to break down the fibers, which reduces the degree of polymerization and releases crystalline cellulose fragments.
2. Neutralization and Washing
Benefits and Safety
One of the key benefits of MCC is its non-digestibility, making it a low-calorie additive suitable for various dietary needs. It is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory authorities, ensuring its widespread use in food and pharmaceuticals.
Conclusion
Microcrystalline Cellulose is a remarkable substance with diverse applications across multiple industries. Its unique properties make it an essential component in pharmaceuticals and food production, contributing to the quality and effectiveness of many products we use daily.




